This is a republication of this blog post
As of a few weeks ago, a cross-platform Windows resource compiler called resinator that I've been working on has been merged into the Zig compiler. This means that the latest master version of Zig can now compile (and cross-compile) Windows resource-definition script (.rc) files for you and link the resulting .res into your program. In addition, the PE/COFF resource table is also used for embedded .manifest files, so Zig now has support for those as well.
If you have no idea what a .rc or .manifest file is, don't worry! The next section should get you up to speed.
Note: I gave a talk about
resinatora little while back if you're interested in some details about its development (apologies for the poor audio)
Use case: an existing C program
To give you an idea of what's possible with this new capability, let's take an existing Windows GUI program written in C and compile it using Zig. I've chosen Rufus for this purpose for a few reasons:
- It is a self-contained, straightforward C program with no external dependencies
- It relies on both its
.rcand.manifestfile for a hefty chunk of its functionality
The first (and really only) step is to write a build.zig file using the existing MinGW/Visual Studio build files as a reference, which I've done in a fork here.
Note: a few workarounds were needed to get things working with the
clangcompiler (which Zig uses under-the-hood for compiling C).
However, before we jump into compiling it, let's first try compiling without using the .rc and .manifest files by commenting out a few lines of the build.zig:
const exe = b.addExecutable(.{
.name = "rufus",
.target = target,
.optimize = optimize,
.link_libc = true,
// .win32_manifest = .{ .path = "src/rufus.manifest" },
});
// exe.addWin32ResourceFile(.{
// .file = .{ .path = "src/rufus.rc" },
// .flags = &.{ "/D_UNICODE", "/DUNICODE" },
// });
Then, to compile it (assuming we're on Windows; we'll handle compiling on non-Windows hosts later):
zig build
But when we try to run it:
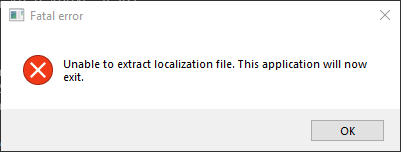
.rc/.manifest fails to load
It turns out that Rufus embeds all of its localization strings as a resource via the rufus.rc file here:
IDR_LC_RUFUS_LOC RCDATA "../res/loc/embedded.loc"
Note: A Windows resource-definition file (
.rc) is made up of both C/C++ preprocessor directives and resource definitions. Resource definitions typically look something like<id> <type> <filepath>or<id> <type> BEGIN <...> END.
Instead of restoring the entire .rc file at once, though, let's start building the .rc file back up piece-by-piece as needed to get a sense of everything the .rc file is being used for. To fix this particular error, we can start with this in rufus.rc:
// this include is needed to #define IDR_LC_RUFUS_LOC
#include "resource.h"
IDR_LC_RUFUS_LOC RCDATA "../res/loc/embedded.loc"
Note: This is adding a
RCDATAresource with IDIDR_LC_RUFUS_LOC(which is set to the integer500via a#defineinresource.h) that gets its data from the file../res/loc/embedded.loc. TheRCDATAresource is used to embed artibrary data into the executable (similar in purpose to Zig's@embedFile)--the contents of theembedded.locfile can then be loaded at runtime viaFindResource/LoadResource.
With this .rc file and the exe.addWin32ResourceFile call uncommented in the build.zig file, we can build again, but when we try to run now we hit:
We'll deal with this properly later, but for now we can bypass this issue by right clicking on rufus.exe and choosing Run as administrator. When we do that, we then hit:
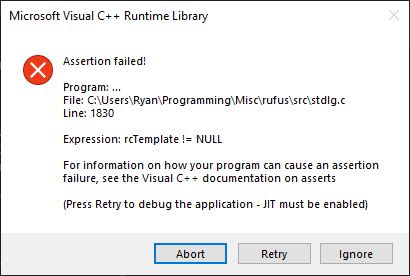
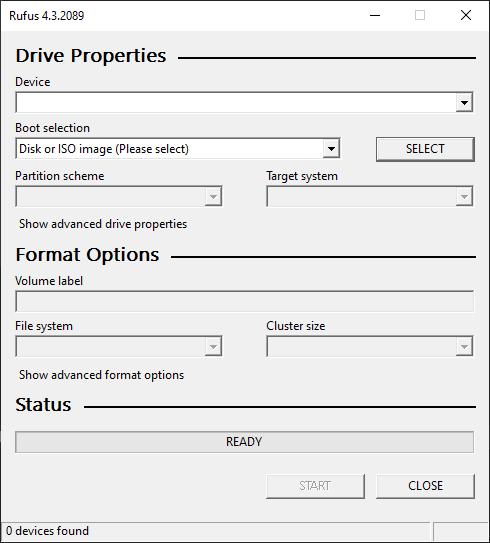
This assertion failure is from Rufus failing to load a dialog template, since Rufus defines all of its dialogs in the .rc file and then loads them at runtime. Here's an example from the .rc file (this is the definition for the main window of Rufus):
IDD_DIALOG DIALOGEX 12, 12, 232, 326
STYLE DS_SETFONT | DS_MODALFRAME | DS_CENTER | WS_MINIMIZEBOX | WS_POPUP | WS_CAPTION | WS_SYSMENU
EXSTYLE WS_EX_ACCEPTFILES
CAPTION "Rufus 4.3.2089"
FONT 9, "Segoe UI Symbol", 400, 0, 0x0
BEGIN
LTEXT "Drive Properties",IDS_DRIVE_PROPERTIES_TXT,8,6,53,12,NOT WS_GROUP
LTEXT "Device",IDS_DEVICE_TXT,8,21,216,8
COMBOBOX IDC_DEVICE,8,30,196,10,CBS_DROPDOWNLIST | WS_VSCROLL | WS_TABSTOP
PUSHBUTTON "...",IDC_SAVE,210,30,14,12,BS_FLAT | NOT WS_VISIBLE
// ... (truncated) ...
END
So let's add back in all the DIALOGEX resource definitions and some necessary preprocessor directives to the .rc file and rebuild:
// Necessary for constants like DS_MODALFRAME, WS_VISIBLE, etc
#include "windows.h"
#ifndef IDC_STATIC
#define IDC_STATIC -1
#endif
// <all the DIALOGEX resource definitions>
Now when we run it:
But things still aren't quite right--at the very least, it's missing the application icon in the title bar. Here's the relevant part of the .rc file:
// Icon with lowest ID value placed first to ensure application icon
// remains consistent on all systems.
IDI_ICON ICON "../res/rufus.ico"
Adding that back into the .rc file, it starts looking a bit more like it should:
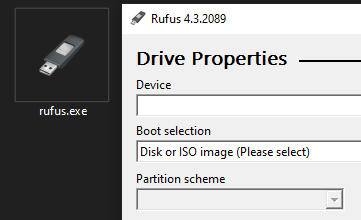
The rest of the .rc file doesn't affect things in an immediately apparent way, so let's speed through it:
- A
VERSIONINFOresource that provides information that then shows up in thePropertieswindow for the executable - Some
RCDATAresources for.pngbutton icons - Some
RCDATAresources for different.SYS,.img, etc. files that Rufus needs for writing bootable media - An
RCDATAresource that is actually an.exefile that Rufus loads and executes at runtime to get better console behavior (see this subdirectory for the details)
So now we can restore the full rufus.rc file and move on to the rufus.manifest file.
Note: A
.manifestfile is an XML file that can be embedded into an executable as a special resource type (it is embedded as a string of XML; there's no conversion to a binary format). Windows then reads the embedded XML and modifies certain attributes of the executable as needed.
First, let's get back to this problem that we bypassed earlier:
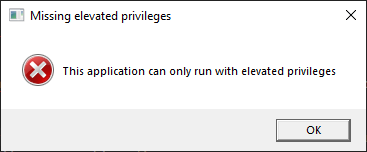
This is something that the .manifest file handles for us. In particular:
<trustInfo xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v3">
<security>
<requestedPrivileges>
<requestedExecutionLevel
level="requireAdministrator"
uiAccess="false"/>
</requestedPrivileges>
</security>
</trustInfo>
This will make Windows aware that the program must be run as administrator, and it'll get this little icon overlayed on it in the file explorer:
Now when we run it, it'll always try to run with administrator privileges.
Next, I mentioned previously that things still didn't look quite right. That's because the .manifest file is also used to set the "version" of the common controls that should be used (e.g. the style of things like buttons, dropdowns, etc). Rufus uses version 6.0.0.0 of the common controls:
<dependency>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity
type="win32"
name="Microsoft.Windows.Common-Controls"
version="6.0.0.0"
processorArchitecture="*"
publicKeyToken="6595b64144ccf1df"
language="*"
/>
</dependentAssembly>
</dependency>
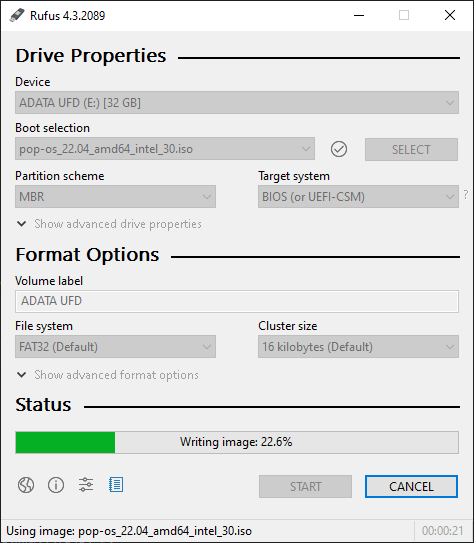
When this is included in the .manifest, everything starts looking as it should (and the .png icons for buttons that were in the .rc file actually show up now):
6.0.0.0
There's a few more things that Rufus uses the .manifest file for that I won't go into detail on:
- Setting the "active code page" to UTF-8
- Setting "DPI Aware" to
true - Removing
MAX_PATHrestrictions - A mild complaint about Microsoft
Finally, we can restore the full .manifest file and compile the complete program.
zig build
Cross-compiling
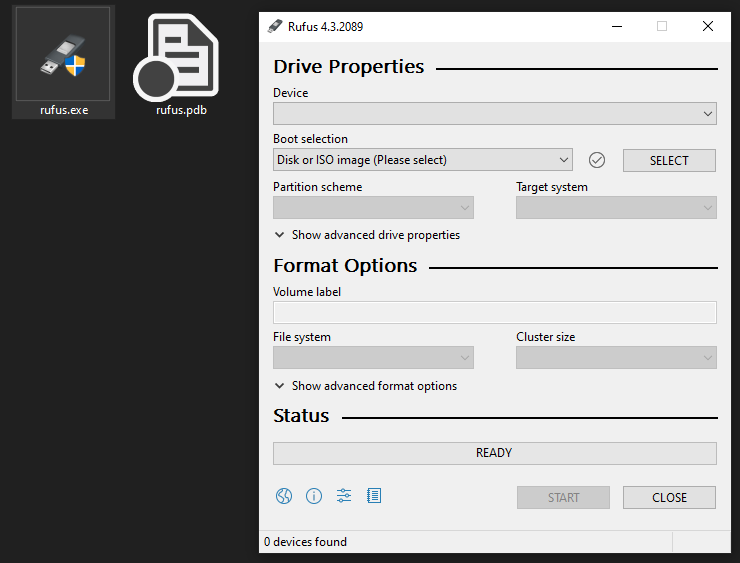
This is all pretty cool, but since the default Windows target ABI is gnu (meaning MinGW) and we've gotten that to work when the host is Windows, we can now cross-compile Rufus from any host system that Zig supports. This means that with only a Zig installation (and nothing else; Zig itself has no external dependencies), we get cross-compilation for free (just need to specify the target):
$ uname
Linux
$ git clone https://github.com/squeek502/rufus
$ cd rufus
$ zig build -Dtarget=x86_64-windows-gnu
$ ls zig-out/bin
rufus.exe rufus.pdb
(above) Cross-compiling Rufus from Linux...
A summary
To recap, here's the list of the consequential things that Rufus relies on its .rc/.manifest files for:
- The layout and style of every dialog in the program (e.g. every button, label, dropdown, etc)
- Localized strings for 30+ different languages
- Icons both for the executable itself and for buttons in its GUI
- Ensuring that the program is run as administrator
and Zig is now capable of compiling (and cross-compiling) programs with these requirements.
Use case: a Zig project
A while back I wrote a Windows shell extension in Zig to mark files as 'watched' in the file explorer. It compiles into a .dll with exactly 1 embedded resource: an icon that gets overlayed on the files that have been marked as 'watched.' The .rc file is incredibly simple:
1 ICON "watched.ico"
Before, I had to compile the .rc file into a .res file using a separate resource compiler (rc.exe, windres, llvm-rc, or resinator), commit the .res file into the repository, and link it into the .dll like this:
watched.addObjectFile(.{ .path = "res/resource.res" });
With Zig's new resource compiling capabilities, I can delete the .res file from the repository and instead go with:
watched.addWin32ResourceFile(.{ .file = .{ .path = "res/resource.rc" } });
(here's the commit where this change was made)
Some benefits of this:
- No longer have a binary
.resfile committed to the repository - No dependency on an external resource compiler when making changes to the resource file
-
.rccompilation fully integrates with the Zig cache system, meaning that if the.rcfile or any of its dependencies changes (e.g#included files or files that are referenced by resource definitions), then the.reswill be recompiled (and otherwise it'll use the cached.res)
The details: How do you use resource files in Zig?
First, it must be noted that UTF-16 encoded .rc files are not supported, since the clang preprocessor does not support UTF-16 encoded files. Unfortunately, UTF-16 encoded .rc files are fairly common, as Visual Studio generates them. Support for UTF-16 files in resinator would likely involve a custom preprocessor, so it's still quite a way off.
Note: If you encounter a UTF-16 encoded
.rcfile, you have a few options to deal with it:
- If the file contains only characters within the Windows-1252 range, then converting the file to Windows-1252 would be the way to go, since Windows-1252 is the default code page when compiling
.rcfiles.- If the file contains characters outside the Windows-1252 range, then the file can be converted to UTF-8 and the flag
/c65001or the preprocessor directive#pragma code_page(65001)can be used (65001 is the code page for UTF-8).
With that out of the way, there are two interfaces to resinator in the Zig compiler:
Via zig build-exe, build.zig, etc
In the simplest form, you can just give the path to the .rc file via the command line like any other source file:
zig build-exe main.zig my_resource_file.rc
Note: If cross-compiling, then
-targetwould need to be specified, e.g.-target x86_64-windows-gnu
the equivalent in build.zig would be:
exe.addWin32ResourceFile(.{ .file = .{ .path = "my_resource_file.rc" } });
If you need to pass rc.exe-like flags, -rcflags <flags> -- can be used before the .rc file like so:
zig build-exe main.zig -rcflags /c65001 -- my_resource_file.rc
the equivalent in build.zig would be:
exe.addWin32ResourceFile(.{
.file = .{ .path = "my_resource_file.rc" },
// Anything that rc.exe accepts will work here
// https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/menurc/using-rc-the-rc-command-line-
// This sets the default code page to UTF-8
.flags = &.{"/c65001"},
});
By default, zig will try to use the most appropriate system headers available (independent of the target ABI). On Windows, it will always try to use MSVC/Windows SDK include paths if they exist, and fall back to the MinGW headers bundled with Zig if not. On non-Windows, it will always use the MinGW header include paths. The intention with this is to make most .rc files work by default whenever possible, since the MSVC includes have some .rc-related include files that MinGW does not.
If the default header include behavior is unwanted, the -rcincludes option can be used:
zig build-exe main.zig my_resource_file.rc -rcincludes=none
the equivalent in build.zig would be:
exe.rc_includes = .none;
The possible values are any (this is the default), msvc (always use MSVC, no fall back), gnu (always use MinGW), or none (no system include paths provided automatically).
Note: If the target object file is not
coff, then specifying a.rcor.resfile on the command line is an error:
$ zig build-exe main.zig zig.rc -target x86_64-linux-gnu
error: rc files are not allowed unless the target object format is coff (Windows/UEFI)
But
std.Build.Compile.Step.addWin32ResourceFilecan be used regardless of the target, and if the target object format is not COFF, then the resource file will just be ignored.
.manifest files
Similar to .rc files, .manifest files can be passed via the command line like so:
zig build-exe main.zig main.manifest
(on the command line, specifying a .manifest file when the target object format is not COFF is an error)
Note: Windows manifest files must have the extension
.manifest; the extension.xmlis not accepted.
or in build.zig:
const exe = b.addExecutable(.{
.name = "manifest-test",
.root_source_file = .{ .path = "main.zig" },
.target = target,
.optimize = optimize,
.win32_manifest = .{ .path = "main.manifest" },
});
(in build.zig, the manifest file is ignored if the target object format is not COFF)
Note: Currently, only one manifest file can be specified per compilation. This is because the ID of the manifest resource is currently always 1 (
CREATEPROCESS_MANIFEST_RESOURCE_ID). Specifying multiple manifests could be supported if a way for the user to specify an ID for each manifest is added (manifest IDs must be au16). I'm not yet familiar enough with manifests to know what the use case for multiple manifests is.
Via zig rc
Similar to how zig cc is a drop-in replacement for a C/C++ compiler, zig rc is a (cross-platform) drop-in replacement for rc.exe. It is functionally identical to standalone resinator, but without the dependency on an external preprocessor.
Here's the usage/help text (note that - and -- are also accepted option prefixes in addition to /):
$ zig rc /?
Usage: zig rc [options] [--] <INPUT> [<OUTPUT>]
The sequence -- can be used to signify when to stop parsing options.
This is necessary when the input path begins with a forward slash.
Supported Win32 RC Options:
/?, /h Print this help and exit.
/v Verbose (print progress messages).
/d <name>[=<value>] Define a symbol (during preprocessing).
/u <name> Undefine a symbol (during preprocessing).
/fo <value> Specify output file path.
/l <value> Set default language using hexadecimal id (ex: 409).
/ln <value> Set default language using language name (ex: en-us).
/i <value> Add an include path.
/x Ignore INCLUDE environment variable.
/c <value> Set default code page (ex: 65001).
/w Warn on invalid code page in .rc (instead of error).
/y Suppress warnings for duplicate control IDs.
/n Null-terminate all strings in string tables.
/sl <value> Specify string literal length limit in percentage (1-100)
where 100 corresponds to a limit of 8192. If the /sl
option is not specified, the default limit is 4097.
/p Only run the preprocessor and output a .rcpp file.
No-op Win32 RC Options:
/nologo, /a, /r Options that are recognized but do nothing.
Unsupported Win32 RC Options:
/fm, /q, /g, /gn, /g1, /g2 Unsupported MUI-related options.
/?c, /hc, /t, /tp:<prefix>, Unsupported LCX/LCE-related options.
/tn, /tm, /tc, /tw, /te,
/ti, /ta
/z Unsupported font-substitution-related option.
/s Unsupported HWB-related option.
Custom Options (resinator-specific):
/:no-preprocess Do not run the preprocessor.
/:debug Output the preprocessed .rc file and the parsed AST.
/:auto-includes <value> Set the automatic include path detection behavior.
any (default) Use MSVC if available, fall back to MinGW
msvc Use MSVC include paths (must be present on the system)
gnu Use MinGW include paths (requires Zig as the preprocessor)
none Do not use any autodetected include paths
Note: For compatibility reasons, all custom options start with :
To give you an idea of how compatible zig rc is with rc.exe, I wrote a set of scripts that tests resource compilers using the .rc files in Microsoft's Windows-classic-samples repository. For each .rc file, it compiles it once with rc.exe (the 'canonical' implementation), and once with each resource compiler under test. Any differences in the .res output are considered a 'discrepancy' and we get a summary of all the found discrepancies at the end.
Here are the results:
Processed 460 .rc files
---------------------------
zig rc
---------------------------
460 .rc files processed without discrepancies
identical .res outputs: 460
---------------------------
That is, zig rc compiles every .rc file into a byte-for-byte identical .res file when compared to rc.exe (see the README for windres and llvm-rc results).
Note: This byte-for-byte compatibility also holds when compiling
.rcfiles viazig build-exe,zig build, etc
Diving deeper: How does it work under-the-hood?
For .rc files, there is a four step process:
- The CLI flags are parsed by resinator. If there are any invalid flags it'll error and fail the compilation
- The
.rcfile is run through theclangpreprocessor and turned into an intermediate.rcppfile - The
.rcppfile is compiled by resinator and turned into a.resfile - The
.resfile is added to the list of link objects and linked into the final binary by the linker
For .manifest files, the process is similar but there's a generated .rc file involved:
- A
.rcfile is generated with the contents1 24 "path-to-manifest.manifest"(1isCREATEPROCESS_MANIFEST_RESOURCE_IDwhich is the default ID for embedded manifests, and24isRT_MANIFEST--there's no recognized keyword for theRT_MANIFESTresource type so the integer value must be used instead) - That generated
.rcfile is compiled into a.resfile (no need for flags/preprocessing) - The
.resfile is linked into the final binary
Wrapping up
I believe that Zig now has the most rc.exe-compatible cross-platform Windows resource compiler implementation out there. With Zig's already powerful zig cc and cross-compilation abilities, this should unlock even more use-cases for Zig--both as a language and as a toolchain.





Top comments (2)
Thanks for sharing, you can also set this post as a re-post in the metadata, this will add an extra line at the top of the page and istruct RSS readers where to find the original version (I think)
Thanks for the heads up, went ahead and set that.